Body Mass Index BMI
The body mass index (BMI) or Quetelet index is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of an individual. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is universally expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres.
BMI calculator for adults  BMI calculator for chidlren BMI calculator for chidlren
What your BMI means
Once you have calculated your BMI, you can work out your healthy weight range.
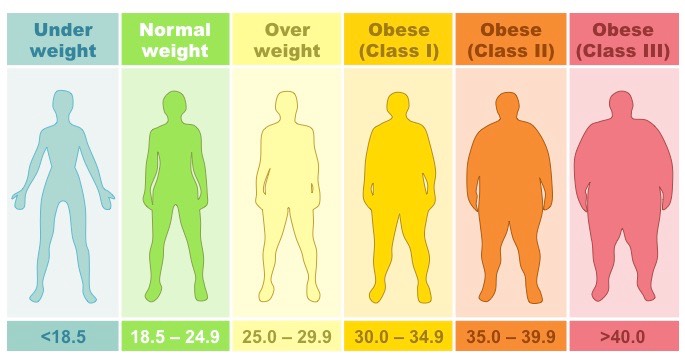
If you have a BMI of:- Under 18.5 – you are considered underweight and possibly malnourished.
- 18.5 to 24.9 – you are within a healthy weight range for young and middle-aged adults.
- 25.0 to 29.9 – you are considered overweight.
- Over 30 – you are considered obese.
For older Australians over the age of 70 years, general health status may be more important than being mildly overweight. Some researchers have suggested that a BMI range of 22-26 is desirable for older Australians.
Some exceptions to the BMI rule
BMI does not differentiate between body fat and muscle mass. This means there are some exceptions to the BMI guidelines, including:- Muscles – body builders and people who have a lot of muscle bulk will have a high BMI, but are not overweight.
- Physical disabilities – people who have a physical disability and are unable to walk may have muscle wasting. Their BMI may be slightly lower, but this does not necessarily mean they are underweight. In these instances, it is important to consult a dietitian who will provide helpful advice.
- Height – BMI is not totally independent of height and it tends to overestimate obesity among shorter people and underestimate it among taller people. Therefore, BMI should not be used as a guide for adults who are very short (less than 150 cm) or very tall (more than 190 cm).
- People of different ethnic groups – Asians and Indians, for example, have more body fat at any given BMI compared to people of European descent. Therefore, the cut-offs for overweight and obesity may need to be lower for these populations. This is because an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease begins at a BMI as low as 23 in Asian populations. Some populations have equivalent risks at a higher BMI, such as people of Torres Strait Islander and Maori origin.
Index of general public information |

 BMI calculator for chidlren
BMI calculator for chidlren














